
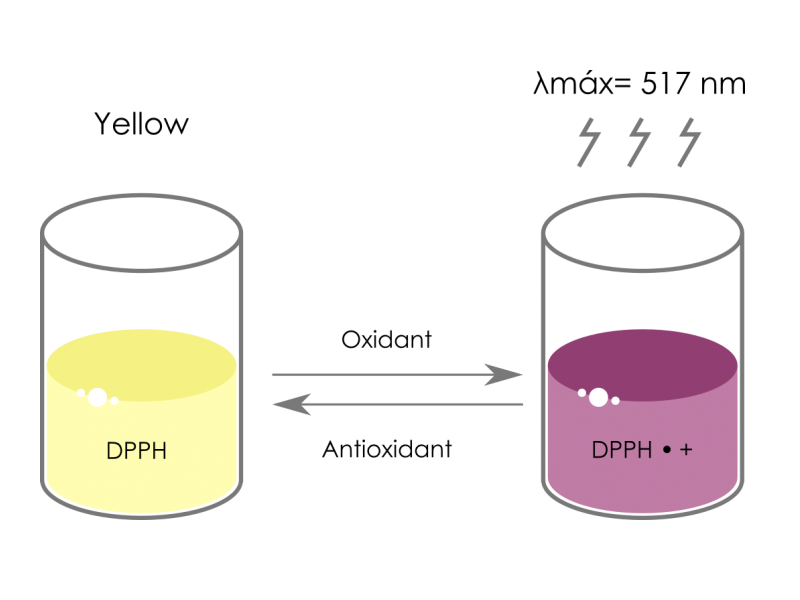
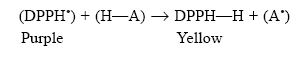
They determine the delay of radical generation as well as the ability to scavenge the radical. Three assays use the delay in oxidation and determine the lag phase as parameter for the antioxidant activity (TEAC I, TRAP, PCL). Another difference between these tests is the reaction procedure. Five methods use organic radical producers (TEAC I-III, TRAP, DPPH, DMPD, PCL) and one method works with metal ions for oxidation (FRAP). The six methods presented can be divided into two groups depending on the oxidising reagent. The antioxidants included gallic acid representing the group of polyphenols, uric acid as the main antioxidant in human plasma, ascorbic acid as a vitamin widely spread in fruits and Trolox ® as water soluble vitamin E analogue. In this study, six common tests for measuring antioxidant activity were evaluated by comparing four antioxidants and applying them to beverages (tea and juices): Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity assay (TEAC I-III assay), Total radical-trapping antioxidant parameter assay (TRAP assay), 2,2-diphenyl- l -picrylhydrazyl assay (DPPH assay), N, N -dimethyl- p -phenylendiamine assay (DMPD assay), Photochemiluminescence assay (PCL assay) and Ferric reducing ability of plasma assay (FRAP assay).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
